NGC 6960 - CirrusnebelNGC 6960 - Veil Nebula
 Fahre mit der Maus über das Bild um es zu vergrössern
Move the mouse over the image to enlarge it
Fahre mit der Maus über das Bild um es zu vergrössern
Move the mouse over the image to enlarge it
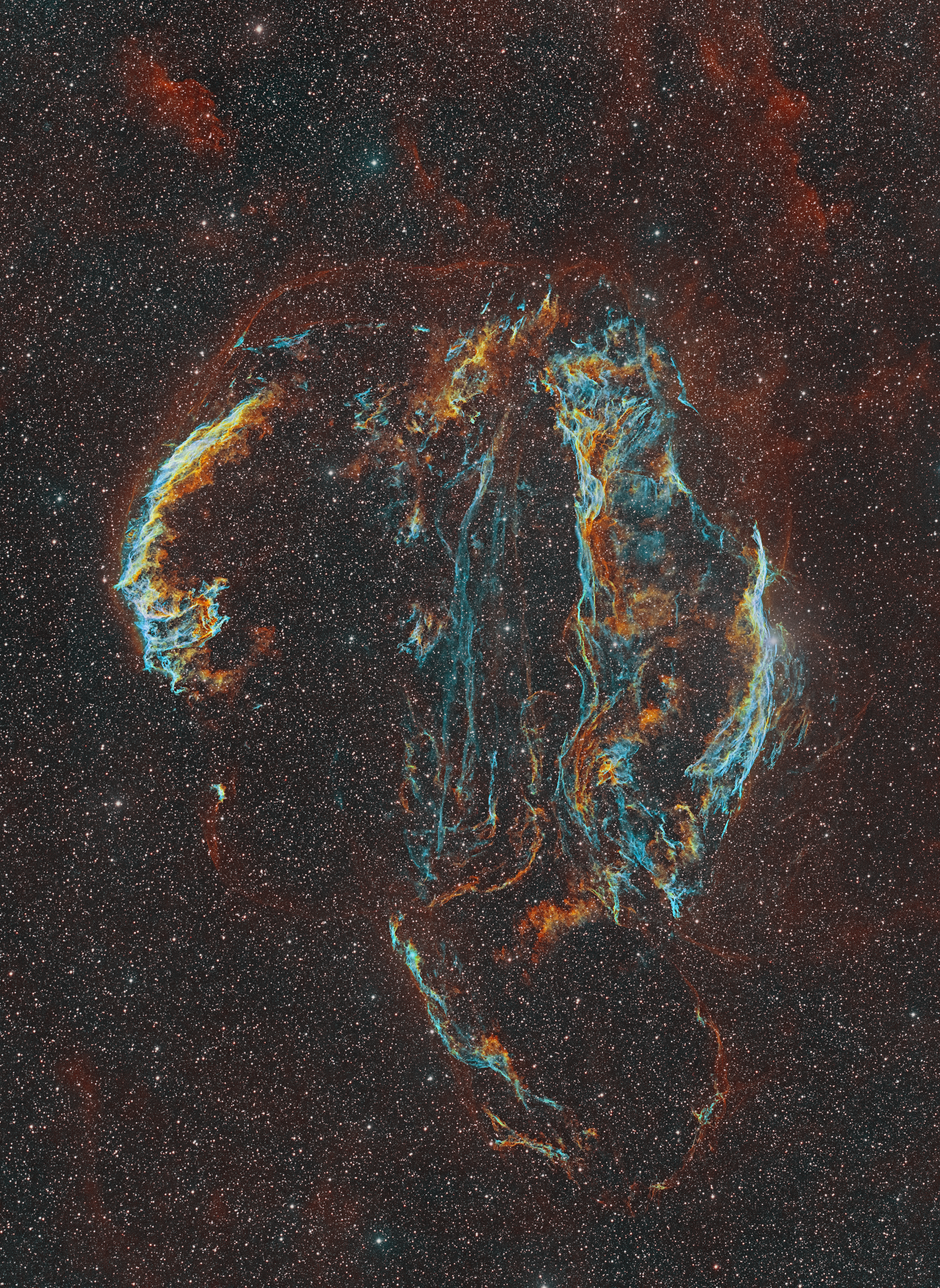
Der Cirrusnebel (auch als Schleier-Nebel, englisch Veil nebula bezeichnet) ist der im optischen Spektrum sichtbare Teil des Cygnusbogens, einer Ansammlung von Emissions- und Reflexionsnebeln, die sich in einer Entfernung von rund 2400 Lichtjahren im Sternbild Schwan befinden. Sie sind zusammen der Überrest einer Supernova, die vor ca. 8.000 Jahren stattfand.
Quelle der Beschreibung: Wikipediahe Veil Nebula is a cloud of heated and ionized gas and dust in the constellation Cygnus.
It constitutes the visible portions of the Cygnus Loop, a supernova remnant, many portions of which have acquired their own individual names and catalogue identifiers. The source supernova was a star 20 times more massive than the Sun which exploded between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. At the time of explosion, the supernova would have appeared brighter than Venus in the sky, and visible in daytime. The remnants have since expanded to cover an area of the sky roughly 3 degrees in diameter (about 6 times the diameter, and 36 times the area, of the full Moon). While previous distance estimates have ranged from 1200 to 5800 light-years, a recent determination of 2400 light-years is based on direct astrometric measurements. (The distance estimates affect also the estimates of size and age.)
Source of description: WikipediaAufnahmedetails Acquisition details
Frames:
Aufnahmedauer insgesamt: Total integration time: 19h 10m
Verwendete Ausrüstung Equipment used